Loading... Please wait...
Loading... Please wait...Categories
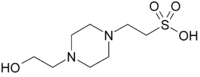
HEPES, Free Acid
(N-[2-Hydroxyethyl]piperazine-N'-[2-Ethanesulfonic Acid]; 4-(2-Hydroxyethyl)piperazine-1-ethanesulfonic acid)
Purity > 99.5%
| CAS Number: |
7365-45-9
|
| Chemical Formula: |
C8H18N2O4S
|
| Molecular Weight: |
238.3 g/mol
|
HEPES is a zwitterionic organic chemical buffering agent. HEPES is commonly added to media at concentrations ranging from 10 mM to 25 mM. Concentrations greater than 50 mM are not recommended since it can result in cell toxicity.
Depending on your application the use of HEPES with Cu(II) should be carefully considered as a possible interaction may occur1.
Recently, HEPES has found an increasing role outside the area of biochemisty such as in the field of nanoparticles2,3,4,5.
Buffering pH range 6.8 - 8.2.
Free Shipping within the Continental USA
HEPES Specifications
Made in the USA in a FDA Registered facility
| Purity: |
99.5%
|
99.0%
|
98.0%
|
| Identification (IR): |
Passes Test
|
Passes Test
|
Passes Test
|
| Absorbance 250nm: |
0.050 a.u. maximum
|
0.060 a.u. maximum
|
|
| Absorbance 260nm: |
0.050 a.u. maximum
|
0.060 a.u. maximum
|
|
| Absorbance 280nm: |
0.080 a.u. maximum
|
0.080 a.u. maximum
|
|
| Heavy Metals: |
1ppm maximum
|
|
|
| Insoluble Matter: |
0.01% maximum
|
|
|
| Loss on Drying: |
0.5% maximum
|
|
|
| pH (5% solution): |
5.0-6.5
|
5.0-6.5
|
|
| pKa: |
7.45-7.65
|
|
|
| Sulfate: |
0.005% maximum
|
|
|
| Trace Metals As: |
5 ppm maximum
|
|
|
| Trace Metals Cu: |
5 ppm maximum
|
|
|
| Trace Metals Fe: |
5 ppm maximum
|
|
|
| Trace Metals Pb: |
5 ppm maximum
|
|
|
Comparable Items:
| Alfa Aesar | J62688-AP |
| Alfa Aesar | J61239-AK |
| Alfa Aesar | A14777-09 |
| Alfa Aesar | J60064-AK |
| Alfa Aesar | A14777-18 |
| Alfa Aesar | J63043-AP |
| Alfa Aesar | J63578-AK |
| Alfa Aesar | A14777-30 |
| Alfa Aesar | J63043-AK |
| Alfa Aesar | J63578-AP |
| Alfa Aesar | J60753-AK |
| Alfa Aesar | J60753-AP |
| Alfa Aesar | J62688-AK |
| Alfa Aesar | J63614-AK |
| Alfa Aesar | J61239-AP |
| Alfa Aesar | J60064-AE |
| Alfa Aesar | J63614-AE |
| Amresco | 0511-50G |
| Amresco | 0511-1KG |
| Amresco | 0511-250G |
| Avantor | 4808-02 |
| EMD Millipore | 5340-5KG |
| EMD Millipore | 5310-100GM |
| EMD Millipore | 5330-1KG |
| EMD Millipore | 5320-500GM |
| G-Biosciences | RC-060 |
| G-Biosciences | RC-061 |
| G-Biosciences | RC-121 |
| JT Baker | 4808-06 |
| JT Baker | 4808-04 |
| Spectrum Chemicals | HE155-12KG |
| Spectrum Chemicals | H1089-100GM |
| Spectrum Chemicals | HE155-500GM |
| Spectrum Chemicals | HE155-100GM |
| Spectrum Chemicals | H1089-250GM |
| Spectrum Chemicals | HE155-1KG |
| Spectrum Chemicals | H1089-25GM |
| Spectrum Chemicals | H1089-5KGBL |
Celebrity Endorsements
1) Hegetschweiler and Saltman, Interaction of copper(II) with N-(2-hydroxyethyl)piperazine-N'-ethanesulfonic acid (HEPES), Inorg. Chem., 1986, 25 (1), pp 107–109.
DOI: 10.1021/ic00221a028
2) Tan, et. al., Synthesis of positively charged silver nanoparticles via photoreduction of AgNO3 in branched polyethyleneimine/HEPES solutions, Langmuir, 2007, 23 (19), pp 9836–9843
DOI: 10.1021/la701236v
3) Sun, et. al. Silver nanoparticles fabricated in Hepes buffer exhibit cytoprotective activities toward HIV-1 infected cells, Chem. Commun., 2005, 5059-5061
DOI: 10.1039/B510984A
4) Govender, et. al. PLGA nanoparticles prepared by nanoprecipitation: drug loading and release studies of a water soluble drug, Journal of Controlled Release, Volume 57, Issue 2, 1 February 1999, Pages 171–185
5) Xie, et. al. Seedless, surfactantless, high-yield synthesis of branched gold nanocrystals in HEPES buffer solution, Chem. Mater., 2007, 19 (11), pp 2823–2830
DOI: 10.1021/cm0700100
Additional Articles of Interest:
Good, N.E.; Winget, D.G.; Winter, W.; Connolly, T.N.; Izawa, S.; Singh, R.M.M. (1966) Hydrogen Ion Buffers for Bifological Research. Biochemistry. Vol. 5., No. 2., 467-477.
-The classic paper, which opened the door to now apatly named Good’s Buffers. The paper examines, twelve new or little used hydrogen ion buffers (at the time) covering the range pKa = 6.15-8.35 have been prepared and tested. Ten are zwitterionic: amino acids, either N-substituted taurines or N-substituted glycines, and two are cationic primary aliphatic amines. All of the zwitterionic buffers are better than conventional buffers in the Hill reaction and in the phosphorylation coupled oxidation of succinate by bean mitochondria.
Xie, J.; Lee, Y.J.; Wang, D.I.C. (2007) Seedless, surfactantless, high-yield synthesis of branched gold nanocrystals in HEPES buffer solution. Chem. Mater., 19 (11), pp 2823–2830.
-In this work, three-dimensional branched gold nanocrystals were produced at high yield by reacting an aqueous solution of chloroauric acid with a Good's buffer, HEPES, at room temperature. This particular method of preparation was scalable to gram-quantity. The branched nanocrystals containing one to eight tips were stable at room temperature and could be stored as a powder after freeze-drying. They were, however, unstable at higher temperatures and transformed into spherical particles upon boiling.
Lleu, P.L.; Rebel, G. (1991) Interference of Good's buffers and other biological buffers with protein determination. Analytical Biochemistry. Volume 192, 215-218.
-This paper examines the possible interference of low concentrations of Hepes and other buffers commonly used in protein determination was studied. The data show that some of these buffers interfere to differing degrees with protein determination according to the Lowry method. A study of the structure-interference relationship suggests that the group ethanolamine is involved in this interference. No interference was observed when protein was measured using bicinchonic acid at the same concentration as the Lowry reagent.
DOI: 10.1021/ic00221a028
2) Tan, et. al., Synthesis of positively charged silver nanoparticles via photoreduction of AgNO3 in branched polyethyleneimine/HEPES solutions, Langmuir, 2007, 23 (19), pp 9836–9843
DOI: 10.1021/la701236v
3) Sun, et. al. Silver nanoparticles fabricated in Hepes buffer exhibit cytoprotective activities toward HIV-1 infected cells, Chem. Commun., 2005, 5059-5061
DOI: 10.1039/B510984A
4) Govender, et. al. PLGA nanoparticles prepared by nanoprecipitation: drug loading and release studies of a water soluble drug, Journal of Controlled Release, Volume 57, Issue 2, 1 February 1999, Pages 171–185
5) Xie, et. al. Seedless, surfactantless, high-yield synthesis of branched gold nanocrystals in HEPES buffer solution, Chem. Mater., 2007, 19 (11), pp 2823–2830
DOI: 10.1021/cm0700100
Additional Articles of Interest:
Good, N.E.; Winget, D.G.; Winter, W.; Connolly, T.N.; Izawa, S.; Singh, R.M.M. (1966) Hydrogen Ion Buffers for Bifological Research. Biochemistry. Vol. 5., No. 2., 467-477.
-The classic paper, which opened the door to now apatly named Good’s Buffers. The paper examines, twelve new or little used hydrogen ion buffers (at the time) covering the range pKa = 6.15-8.35 have been prepared and tested. Ten are zwitterionic: amino acids, either N-substituted taurines or N-substituted glycines, and two are cationic primary aliphatic amines. All of the zwitterionic buffers are better than conventional buffers in the Hill reaction and in the phosphorylation coupled oxidation of succinate by bean mitochondria.
Xie, J.; Lee, Y.J.; Wang, D.I.C. (2007) Seedless, surfactantless, high-yield synthesis of branched gold nanocrystals in HEPES buffer solution. Chem. Mater., 19 (11), pp 2823–2830.
-In this work, three-dimensional branched gold nanocrystals were produced at high yield by reacting an aqueous solution of chloroauric acid with a Good's buffer, HEPES, at room temperature. This particular method of preparation was scalable to gram-quantity. The branched nanocrystals containing one to eight tips were stable at room temperature and could be stored as a powder after freeze-drying. They were, however, unstable at higher temperatures and transformed into spherical particles upon boiling.
Lleu, P.L.; Rebel, G. (1991) Interference of Good's buffers and other biological buffers with protein determination. Analytical Biochemistry. Volume 192, 215-218.
-This paper examines the possible interference of low concentrations of Hepes and other buffers commonly used in protein determination was studied. The data show that some of these buffers interfere to differing degrees with protein determination according to the Lowry method. A study of the structure-interference relationship suggests that the group ethanolamine is involved in this interference. No interference was observed when protein was measured using bicinchonic acid at the same concentration as the Lowry reagent.