Loading... Please wait...
Loading... Please wait...Categories
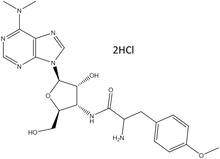
Puromycin Dihydrochloride
Purity > 98.0 %
| CAS Number: |
58-58-2
|
| Chemical Formula: |
C22H29N705 2HCl
|
| Molecular Weight: |
544.4 g/mol
|
Puromycin dihydrochloride is an aminonucleoside antiobiotic and used as a selection agent against cells expressing the pac gene. Inhibits growth of Gram positive bacteria and various animal and insect cells.
Puromycin enters the A site and transfers to the growing chain, causing premature chain release. The exact mechanism of action is unknown at this time, but the 3' position contains an amide linkage instead of the normal ester linkage of tRNA, the amide bond makes the molecule much more resistant to hydrolysis and thus stops the ribosome.
Puromycin Solutions
The concentration of our Puromycin solution is 10mg/ml
1 ml is usally added to 1L of cell culture media with for use as a selection agent at a range of 1-10 μg/mL.
Appearance: White to off-white powder or clear and colorless to light yellow in solution
Store: 2-8°C for powder and -20°C for solution
Solutions are made by Toku E
Free Shipping with the Continental USA
Puromycin Protocol
Background
Puromycin resistant cells express the pac gene which encodes an N-acetyl puromycin transferase. The pac gene can be mobilized on a plasmid and used to transfect a host cell in an attempt to provide resistance; therefore, puromycin can be used in gene selections for mammalian host cells. For this application, a kill curve is typically performed to determine the minimum effective puromycin concentration to kill non-resistant cells.
Preparation and storage
The product is soluble in water (50 mg/ml), yielding a clear, colorless to faint yellow solution. The stock solution may be passed through a 0.22 μm filter and stored in aliquots at –20 °C.
Mammalian Cell Culture
Lentiviral Transduction
1. Add 1.6 x 10^4 cells in fresh media to the number of wells needed for each construct in a 96-well plate. Duplicate or triplicate wells for each lentiviral construct and control should be used. Incubate 18-20 hours at 37°C in a humidified incubator in an atmosphere of 5-7% CO2. Growth rate of cells vary greatly. Adjust the number of cells plated to accommodate a confluency of 70% upon transduction. Also account for the length of time the cells will be growing before downstream analysis when determining the plating density.
2. Remove media from wells. Add 110μl media and Hexadimethrine bromide (final concentration 8 μg/ml) to each well. Gently swirl the plate to mix. Hexadimethrine bromide enhances transduction of most cell types. Some cells, like primary neurons, are sensitive to hexadimethrine bromide. Do not add hexadimethrine bromide to these types of cells. If working with a cell type for the first time, a hexadimethrine control only well should be used to determine cell sensitivity. Add 2-15 μl of lentiviral particles to appropriate wells. Gently swirl the plate to mix.
3. Incubate 18-20 hours at 37°C in a humidified incubator in an atmosphere of 5-7% CO2. When transducing a lentiviral construct into a cell line for the first time, a range of volume or MOI should be tested. 2, 5, 10, and 15 μl of lentiviral particles per 1.6 x 10^4 cells or MOIs of 0.5, 1, and 5 should be used to determine the optimal transduction efficiency and knockdown for each cell line. Transduction efficiency can be optimized using the pLKO.1-Puro. Cells may be incubated for as little as 4 hours before changing the media containing lentiviral particles. Overnight incubation may be avoided when toxicity of the lentiviral particles are a concern.
4. Remove the media containing lentiviral particles from wells. Add fresh media to a volume of 120 μl to each well. For cell types that do not strongly adhere to the plate, 100 μl of media may be removed and replaced with 100 μl fresh media.
5. Remove media from wells. Add fresh media containing puromycin. The appropriate concentration of puromycin for each cell type is different. If the concentration for the desired cell type is unknown, a titration experiment must be performed. Typically, 2-10 μg/ml are sufficient to kill most untransduced mammalian cell types.
6. Replace media with fresh puromycin containing media every 3-4 days until resistant colonies can be identified. Pick a minimum of 5 puromycin-resistant colonies and expand each clone to assay for knockdown of the target gene.
Comparable Items:
| Acros Organics | 22742-0100 |
| Alfa Aesar | J61278-MC |
| Alfa Aesar | J61278-MB |
| Alfa Aesar | J61278-ME |
| EMD Millipore | 540222-100MG |
| EMD Millipore | 540222-25MG |
| EMD Millipore | 540411-100MG |
| EMD Millipore | 540411-25MG |