Loading... Please wait...
Loading... Please wait...Categories
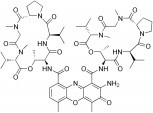
Actinomycin D
(Actinomycin C1; Dactinomycin; Oncostatin K; Actinomycin IV; 2-Amino-N,N'-bis(6,13-diisopropyl-2,5,9-trimethyl-1,4,7,11,14-pentaoxohexadecahydro-1H-pyrrolo[2,1-i][1,4,7,10,13]oxatetraazacyclohexadecin-10-yl)-4,6-dimethyl-3-oxo-3H-phenoxazine-1,9-dicarboxamide)
Purity > 95.0%
| CAS Number: | 50-76-0 |
| Chemical Formula: | C62H86N12O16 |
| Molecular Weight: | 1255.42 g/mol |
Actinomycin is a cyclic polypeptide-containing antibiotic that binds to DNA and inhibits RNA polymerase activity. Because Actinomycin can bind DNA duplexes, it can also interfere with DNA replication, although other chemicals such as hydroxyurea are better suited for use in the laboratory as inhibitors of DNA synthesis.
Actinomycin D and its fluorescent derivative, 7-aminoactinomycin D (7-AAD), are used as stains in microscopy and flow cytometry applications. The affinity of these stains/compounds for GC-rich regions of DNA strands makes them excellent markers for DNA. 7-AAD binds to single stranded DNA; therefore it is a useful tool in determining apoptosis and distinguishing between dead and alive cells.
Actinomycin D Solubility:
| Acetone: | 10 mg/mL |
| Acetonitrile: | 10 mg/mL |
| Water: | 0.5 mg/mL |
| DMSO: | >20 mg/mL |
| 100% Ethanol: | 1 mg/ml |
Comparable Items:
| Acros Organics | 29494-0250 |
| Acros Organics | 29494-0050 |
| Alfa Aesar | J60148-LB0 |
| Amresco | J608-5MG |
| EMD Millipore | 114666-1SET |
| EMD Millipore | 2472-5MG |
| Freudenberg | 1229/10 |
| US Pharmacopeia | 1162400 |
Celebrity Endorsements
Grossa, Paul; Cousineaua, Gilles; 1963. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. Effects of actinomycin D on macromolecule synthesis and early development in sea urchin eggs. Volume 10, Issue 4, 321–326.
Fraschini, A; Bottone, MG; Scovassi, Ai; Denegri, M; Risueño, MC; Testillano, PS; Martin, TE; Biggiogera, M; Pellicciari, C; 2005. Changes in extranucleolar transcription during actinomycin D-induced apoptosis. Histol Histopathol. 2005 Jan;20(1):107-17.
"Actinomycin D (AMD) inhibits DNA-dependent RNA polymerases and its selectivity depends on the concentration used; at very high concentrations it may also induce apoptosis. This study investigates the effects of different concentrations (0.01 to 1 microg/ml) of AMD on RNA transcription and maturation and on the organization of nuclear ribonucleoproteins (RNPs), and their relationship with apoptosis induction."
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8871827
Schöfer C1, Weipoltshammer K, Almeder M, Müller M, Wachtler F. Redistribution of ribosomal DNA after blocking of transcription induced by actinomycin D. Chromosome Res. 1996 Aug;4(5):384-91.
"We report on the effect of different doses and times of incubation of the cytostatic drug actinomycin D (AMD) on nucleolar morphology, rRNA gene transcription and rDNA gene localization using in situ hybridization and the immunocytochemical detection of the human upstream binding factor (UBF) at the electron microscopic level in HeLa cells."
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8871827
Krugh, TR; Chen, YC; Actinomycin D-deoxynucleotide complexes as models for the actinomycin D-DNA complex. The use of nuclear magnetic resonance to determine the stoichiometry and the geometry of the complexes. Biochemistry 12/1975; 14(22):4912-22.
Wu, MH; Yung, BY; Cell cycle phase-dependent cytotoxicity of actinomycin D in HeLa cells. European Journal of Pharmacology 05/1994; 270(2-3):203-12.